As a business owner there are many important decisions to make. Finding the right retirement plan for your business is one of these key decisions. The retirement plan you select can have a large impact on recruiting and retaining great employees, the company tax situation and accelerating retirement savings for owners and employees. Below we explain the features, advantages, and things to consider for the popular retirement plan options.
SEP IRA
Features
Establish an IRA for each eligible employee. All contributions are flexible and made by the employer. The employer may contribute the up to the lesser of 25% compensation or $58,000. Typically, a good plan for a business with less than 10 employees.
Advantages
The company contributions are generally federally tax deductible. SEP IRAs have no requirements on amount or frequency of contributions and are easily established with minimal paperwork. The plan can be established until the extended due date of the employer’s tax return.
Considerations
Does not allow for loans, delayed vesting, or Roth contributions. The employer may also be required to cover employees who would be excluded from a standard 401(k) plan.
SIMPLE IRA
Features
Employees may defer up to $13,500 (plus an additional $3,000 if over age 50). The employer contributes either by matching up to 3% of salary or contributing 2% of all eligible employees’ salary, not contingent on employee contributions.
Advantages
The company contributions are generally federally tax deductible. Simple IRAs have minimal plan expenses, administrative responsibilities, and minimal paperwork. They do not require any compliance testing or form 5500 filing.
Considerations
Simple IRAs do require an annual employer contribution. They offer less flexibility and cannot be used with another qualified plan. Does not allow for loans, vesting or Roth contributions. They must be established between January 1st and October 1st of the calendar year. The employer may also be required to cover employees who would be excluded from a standard 401(k) plan.
401(k) and 403(b)
Features
Popular plan that is typically understood by employees. It is a qualified profit-sharing plan allowing employee to contribute a portion of their wages to an individual account.
Advantages
The company contributions are generally federally tax deductible. They have contribution flexibility and typically benefit key employees. They offer additional profit-sharing contributions that may be subject to vesting. Due to tax savings, coverage, and vesting, some administrative costs may be offset.
Considerations
You will need a high level of participation by non-highly compensated employees to allow maximum salary deferral contributions by the owners and highly compensated employees.
Safe Harbor 401(k)
Features
Offers the same benefits of a traditional 401(k) plan with fewer compliance testing issues. This version may allow higher salary deferral contributions than traditional 401(k) plans, subject to specific employer contributions being made. Employer must either match employee contributions (up to 4% of salary) or make mandatory contributions (3% of salary).
Advantages
The company contributions are generally federally tax deductible. They have contribution flexibility and typically benefit key employees. They offer additional profit-sharing contributions that may be subject to vesting. Due to tax savings, coverage, and vesting, some administrative costs may be offset. Allows for participant loans and hardship withdrawals, giving employees flexibility.
Considerations
Administrative costs may be higher than other plans and requires filing form 5500 and subject to compliance testing. An annual employer contribution and annual employee notice are required.
Solo 401(k)
Features
Solo 401(k)s have no age or income restrictions, but to set up you must be a business owner with no employees (spouse may be included if they have earned income from the business). Can contribute up to $58,000 for 2021 ($6,500 catch-up contribution if over 50). The plan must be established by December 31st of the year you would like to make employee contributions, but employer profit-sharing contributions can be made until your tax-filing deadline.
Advantages
By taking advantage of the high contribution limits as the employee and employer, you could save up to $58,000 for 2021 (depending on compensation/income). If set up as traditional (as opposed to Roth), the contributions are generally federally tax deductible.
Considerations
To open a solo 401(k), you will need an Employer Identification Number (EIN) and complete a plan adoption agreement. Once your plan surpasses $250,000 in assets at year-end, you will be required to file an annual report on Form 5500-SF.
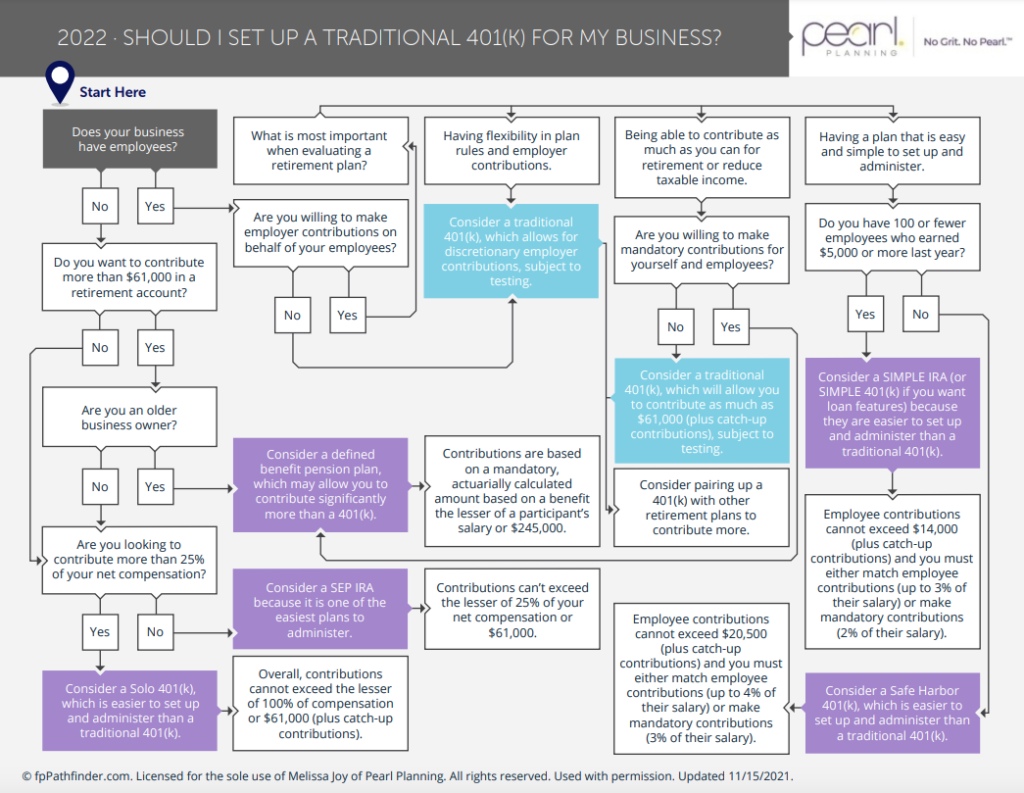
As you can see, there are several options to consider when selecting a retirement plan for your business (and we did not even touch on defined benefit plans!). Take a look at our flow chart to help you determine which plan is best for you. If you want to talk retirement plan options in more detail or are ready to move forward, schedule a meeting here.
While we are familiar with the tax provisions of the issues presented herein, as Financial Advisors of RJFS, we are not qualified to render advice on tax or legal matters. You should discuss tax or legal matters with the appropriate professional.